深入理解k8s中的Event机制
Kubernetes事件(Event)是一种资源对象,用于展示集群内发生的情况。Kubernetes系统中的各个组件会将运行时发生的各种事件(例如,调度器做了什么决定,某些Pod为什么被从节点中驱逐)上报给apiserver。apiserver将Event存储在Etcd内,强制执行保留策略:在最后一次的事件发生后,删除1小时之前发生的事件。
可以通过kubectl get event或kubectl describe pod <podname>命令显示事件
这两个命令均不会显示Event的名字,通过kubectl get events看到的OBJECT也不是Events的真名,而是与该Event相关的资源的名称(格式为pod/{Pod名}、node/{Node名}
Event名为{Pod名}.Unix时间戳、{Node名}.Unix时间戳
k8s.io/api/core/v1/types.go中定义的Event结构体:
type Event struct {
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
metav1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=metadata"`
InvolvedObject ObjectReference `json:"involvedObject" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=involvedObject"` //和哪个资源对象有关
Reason string `json:"reason,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,3,opt,name=reason"` //发生原因
Message string `json:"message,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,4,opt,name=message"` //详细信息
Source EventSource `json:"source,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,5,opt,name=source"` //来源,包括component、host
FirstTimestamp metav1.Time `json:"firstTimestamp,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,6,opt,name=firstTimestamp”`
LastTimestamp metav1.Time `json:"lastTimestamp,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,7,opt,name=lastTimestamp”`
Count int32 `json:"count,omitempty" protobuf:"varint,8,opt,name=count”` //事件发生的次数
Type string `json:"type,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,9,opt,name=type”`
EventTime metav1.MicroTime `json:"eventTime,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,10,opt,name=eventTime”`
Series *EventSeries `json:"series,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,11,opt,name=series"`
Action string `json:"action,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,12,opt,name=action”` //针对此事件已采取何种措施
Related *ObjectReference `json:"related,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,13,opt,name=related"`
ReportingController string `json:"reportingComponent" protobuf:"bytes,14,opt,name=reportingComponent"`
ReportingInstance string `json:"reportingInstance" protobuf:"bytes,15,opt,name=reportingInstance"`
}
定义了两种event类型:
const (
EventTypeNormal string = "Normal"
EventTypeWarning string = "Warning"
)
《k8s源码剖析》中的EventBroadcaster事件管理机制图:
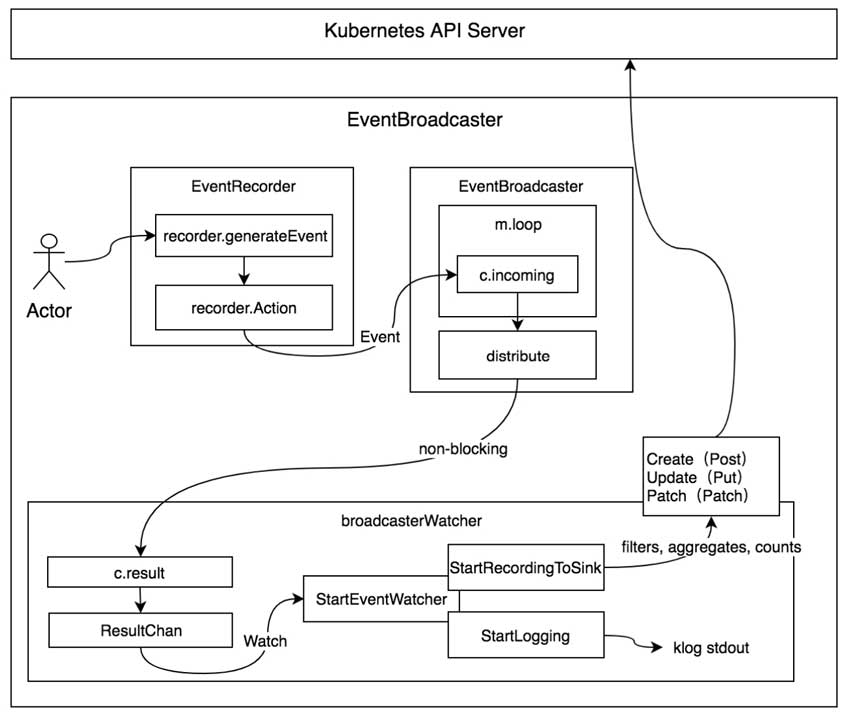
EventRecorder
在client-go中的tools/record/event.go中定义的EventRecorder接口,:
type EventRecorder interface {
Event(object runtime.Object, eventtype, reason, message string)
Eventf(object runtime.Object, eventtype, reason, messageFmt string, args ...interface{}) //通过使用fmt.Sprintf格式化输出事件的格式
AnnotatedEventf(object runtime.Object, annotations map[string]string, eventtype, reason, messageFmt string, args ...interface{}) // 功能与Eventf一样,但附加了注释(Annotations)字段
}
EventRecorder定义了记录Event的三种方法,用以帮助k8s组件记录Event。
结构体recorderImpl是其实现:
type recorderImpl struct {
scheme *runtime.Scheme
source v1.EventSource
*watch.Broadcaster
clock clock.Clock
}
recorderImpl结构体中包含apimachinery/pkg/watch/mux.go中的Broadcaster结构体对象地址,因此可以调用Broadcaster实现的方法
recorderImpl实现了EventRecorder接口定义的三个方法,以Event方法为例,调用链为:
recorderImpl.Event方法→ recorderImpl.generateEvent方法→Broadcaster.ActionOrDrop方法:
func (recorder *recorderImpl) Event(object runtime.Object, eventtype, reason, message string) {
recorder.generateEvent(object, nil, metav1.Now(), eventtype, reason, message)
}
func (recorder *recorderImpl) generateEvent(object runtime.Object, annotations map[string]string, eventtype, reason, message string) {
ref, err := ref.GetReference(recorder.scheme, object)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Could not construct reference to: '%#v' due to: '%v'. Will not report event: '%v' '%v' '%v'", object, err, eventtype, reason, message)
return
}
if !util.ValidateEventType(eventtype) {
klog.Errorf("Unsupported event type: '%v'", eventtype)
return
}
event := recorder.makeEvent(ref, annotations, eventtype, reason, message)
event.Source = recorder.source
if sent := recorder.ActionOrDrop(watch.Added, event); !sent {
klog.Errorf("unable to record event: too many queued events, dropped event %#v", event)
}
}
func (m *Broadcaster) ActionOrDrop(action EventType, obj runtime.Object) bool {
select {
case m.incoming <- Event{action, obj}:
return true
default:
return false
}
}
ActionOrDrop方法将Event写入m.incoming Chan中,完成事件生产过程。
EventBroadcaster
在client-go中的tools/record/event.go中定义了EventBroadcaster接口:
type EventBroadcaster interface {
StartEventWatcher(eventHandler func(*v1.Event)) watch.Interface
StartRecordingToSink(sink EventSink) watch.Interface
StartLogging(logf func(format string, args ...interface{})) watch.Interface
StartStructuredLogging(verbosity klog.Level) watch.Interface
NewRecorder(scheme *runtime.Scheme, source v1.EventSource) EventRecorder
Shutdown()
}
EventBroadcaster作为Event消费者和事件广播器,消费EventRecorder记录的事件并将其分发给目前所有已连接的broadcasterWatcher。
结构体eventBroadcasterImpl是其实现:
type eventBroadcasterImpl struct {
*watch.Broadcaster
sleepDuration time.Duration
options CorrelatorOptions
}
eventBroadcasterImpl结构体中,同样包含Broadcaster结构体对象地址,因此可以调用Broadcaster实现的方法
在apimachinery中的pkg/watch/mux.go中定义了Broadcaster结构体:
type Broadcaster struct {
watchers map[int64]*broadcasterWatcher
nextWatcher int64
distributing sync.WaitGroup
incoming chan Event
stopped chan struct{}
watchQueueLength int
fullChannelBehavior FullChannelBehavior
}
client-go的tools/record/event.go中,提供的实例化eventBroadcasterImpl的函数:
func NewBroadcaster() EventBroadcaster {
return &eventBroadcasterImpl{
Broadcaster: watch.NewBroadcaster(maxQueuedEvents, watch.DropIfChannelFull),
sleepDuration: defaultSleepDuration,
}
}
Broadcaster实际由apimachinery/pkg/watch/mux.go中的NewBroadcaster函数创建:
func NewBroadcaster(queueLength int, fullChannelBehavior FullChannelBehavior) *Broadcaster {
m := &Broadcaster{
watchers: map[int64]*broadcasterWatcher{},
incoming: make(chan Event, incomingQueueLength),
watchQueueLength: queueLength,
fullChannelBehavior: fullChannelBehavior,
}
m.distributing.Add(1)
go m.loop()
return m
}
创建时,会在内部启动goroutine,通过m.loop方法监控m.incoming;同时将监控的事件通过m.distribute函数分发给所有已连接的BroadcasterWatcher:
func (m *Broadcaster) distribute(event Event) {
if m.fullChannelBehavior == DropIfChannelFull {
for _, w := range m.watchers {
select {
case w.result <- event:
case <-w.stopped:
default: // 队列满时,不阻塞
}
}
} else {
for _, w := range m.watchers {
select {
case w.result <- event:
case <-w.stopped:
}
}
}
}
分发过程有两种机制,分别是非阻塞(Non-Blocking)分发机制和阻塞(Blocking)分发机制。
在非阻塞分发机制(默认)下使用DropIfChannelFull标识。DropIfChannelFull标识位于select多路复用中,使用default关键字做非阻塞分发,当w.result缓冲区满的时候,事件会丢失。
在阻塞分发机制下使用WaitIfChannelFull标识。WaitIfChannelFull标识也位于select多路复用中,没有default关键字,当w.result缓冲区满的时候,分发过程会阻塞并等待。
eventBroadcasterImpl实现的两种Event的处理方法:
(1)StartLogging:将事件写入日志中。
func (e *eventBroadcasterImpl) StartLogging(logf func(format string, args ...interface{})) watch.Interface {
return e.StartEventWatcher(
func(e *v1.Event) {
logf("Event(%#v): type: '%v' reason: '%v' %v", e.InvolvedObject, e.Type, e.Reason, e.Message)
})
}
(2)StartRecordingToSink:将事件存储到相应的sink。
func (e *eventBroadcasterImpl) StartRecordingToSink(sink EventSink) watch.Interface {
eventCorrelator := NewEventCorrelatorWithOptions(e.options)
return e.StartEventWatcher(
func(event *v1.Event) {
recordToSink(sink, event, eventCorrelator, e.sleepDuration)
})
}
kubelet默认均使用,也就是说任何一个事件会同时发送给apiserver、打印到日志;用户也可以编写自己的事件处理逻辑。
它们均依赖于StartEventWatcher方法:
func (e *eventBroadcasterImpl) StartEventWatcher(eventHandler func(*v1.Event)) watch.Interface {
watcher := e.Watch() //注册了一个watcher到broadcaster里面
go func() {
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
for watchEvent := range watcher.ResultChan() {
event, ok := watchEvent.Object.(*v1.Event)
if !ok {
continue
}
eventHandler(event)
}
}()
return watcher
}
该函数内部运行了一个goroutine,用于不断监控EventBroadcaster来发现事件并调用传入的eventHandler函数对事件进行处理。
StartLogging传入的eventHandler,只是执行了被传入的logf函数
StartRecordingToSink传入的eventHandler,则根据被传入的sink执行了recordToSink函数:
func recordToSink(sink EventSink, event *v1.Event, eventCorrelator *EventCorrelator, sleepDuration time.Duration) {
eventCopy := *event //处理前先做拷贝,因为可能有其它listener也需要这个Event
event = &eventCopy
result, err := eventCorrelator.EventCorrelate(event)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(err)
}
if result.Skip {
return
}
tries := 0
for {
if recordEvent(sink, result.Event, result.Patch, result.Event.Count > 1, eventCorrelator) { //最终把事件发送到apiserver
break
}
tries++
if tries >= maxTriesPerEvent {
klog.Errorf("Unable to write event '%#v' (retry limit exceeded!)", event)
break
}
if tries == 1 { //第一次同步要错开
time.Sleep(time.Duration(float64(sleepDuration) * rand.Float64()))
} else {
time.Sleep(sleepDuration)
}
}
}
recordToSink方法首先会调用tools/record/events_cache.go中的EventCorrelate方法对event做预处理,聚合相同的事件,避免产生的事件过多,增加sink的压力,如果传入的Event太多了,那么result.Skip处就会返回
func (c *EventCorrelator) EventCorrelate(newEvent *v1.Event) (*EventCorrelateResult, error) {
if newEvent == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("event is nil")
}
aggregateEvent, ckey := c.aggregator.EventAggregate(newEvent)
observedEvent, patch, err := c.logger.eventObserve(aggregateEvent, ckey)
if c.filterFunc(observedEvent) {
return &EventCorrelateResult{Skip: true}, nil
}
return &EventCorrelateResult{Event: observedEvent, Patch: patch}, err
}
接下来会调用recordEvent方法把事件发送到sink,它会重试很多次(默认是12次),并且每次重试都有一定时间间隔(默认是10秒钟)。
func recordEvent(sink EventSink, event *v1.Event, patch []byte, updateExistingEvent bool, eventCorrelator *EventCorrelator) bool {
var newEvent *v1.Event
var err error
if updateExistingEvent { //result.Event.Count > 1时,更新已经存在的事件
newEvent, err = sink.Patch(event, patch)
}
// 创建一个新的事件
if !updateExistingEvent || (updateExistingEvent && util.IsKeyNotFoundError(err)) {
event.ResourceVersion = ""
newEvent, err = sink.Create(event)
}
if err == nil {
eventCorrelator.UpdateState(newEvent)
return true
}
// 如果是已知错误,就不要再重试了;否则,返回false,让上层进行重试
switch err.(type) {
case *restclient.RequestConstructionError:
klog.Errorf("Unable to construct event '%#v': '%v' (will not retry!)", event, err)
return true
case *errors.StatusError:
if errors.IsAlreadyExists(err) {
klog.V(5).Infof("Server rejected event '%#v': '%v' (will not retry!)", event, err)
} else {
klog.Errorf("Server rejected event '%#v': '%v' (will not retry!)", event, err)
}
return true
case *errors.UnexpectedObjectError:
default:
}
klog.Errorf("Unable to write event: '%v' (may retry after sleeping)", err)
return false
}
BroadcasterWatcher
client-go的tools/record/event.go中定义了EventSink接口:
type EventSink interface {
Create(event *v1.Event) (*v1.Event, error)
Update(event *v1.Event) (*v1.Event, error)
Patch(oldEvent *v1.Event, data []byte) (*v1.Event, error)
}
EventSink相当于观察者(Watcher),作为sink从EventBroadcaster接收事件,自定义事件的处理方式
client-go的tools/events/event_broadcaster.go中EventSinkImpl是其具体实现
type EventSinkImpl struct {
Interface typedeventsv1.EventsV1Interface
}
Interface中包含了Restful client,可通过其与k8s apiserver交互
EventSinkImpl实现的这三种方法:
func (e *EventSinkImpl) Create(event *eventsv1.Event) (*eventsv1.Event, error) {
if event.Namespace == "" {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("can't create an event with empty namespace")
}
return e.Interface.Events(event.Namespace).Create(context.TODO(), event, metav1.CreateOptions{})
}
func (e *EventSinkImpl) Update(event *eventsv1.Event) (*eventsv1.Event, error) {
if event.Namespace == "" {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("can't update an event with empty namespace")
}
return e.Interface.Events(event.Namespace).Update(context.TODO(), event, metav1.UpdateOptions{})
}
func (e *EventSinkImpl) Patch(event *eventsv1.Event, data []byte) (*eventsv1.Event, error) {
if event.Namespace == "" {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("can't patch an event with empty namespace")
}
return e.Interface.Events(event.Namespace).Patch(context.TODO(), event.Name, types.StrategicMergePatchType, data, metav1.PatchOptions{})
}
会分别调用Restful client的Create、Update、Patch,将Event上报至apiserver